PhET- Density
Activity- Funsheet
Custom Section Name visualizethis39/penaj
Material
|
Mass (kg)
|
Volume (L)
|
Density (kg/L)
|
Does it Float?
|
Styrofoam
|
2.26 |
15.08 |
.15kg/L |
Yes |
Wood
|
6.03 |
15.08 |
.40kg/L |
Yes |
Ice
|
13.85 |
15.08 |
.92kg/L |
Yes |
Brick
|
30.15 |
15.08
|
2.00kg/L |
No |
Aluminum
|
40.70 |
15.08 |
2.70kg/L |
No |
1.
In the custom setting, choose the ‘My Object’ option
in the material drop down box. Set the
mass of your object to 4 kg. Adjust the volume
to find the minimum volume needed to make the object float.
Volume____4.17_____________ Density_____.96kg/L_____________
2. How does the density of a large piece of aluminum compare to a small piece?
Density remains the same.
Same Mass Section
Material
|
Mass (kg)
|
Volume (L)
|
Density (kg/L)
|
Does it Float?
|
Blue
|
5.00kg |
105.00L |
47.619 |
No |
Yellow
|
5.00kg |
105.00L |
47.619 |
Yes |
Green
|
5.00kg |
102.50L |
48.78 |
No |
Red
|
5.00kg |
101.25L |
49.382 |
No |
Same Volume Section
Material
|
Mass (kg)
|
Volume (L)
|
Density (kg/L)
|
Does it Float?
|
Blue
|
6.00kg |
105.00L |
57.14 |
No |
Yellow
|
8.00kg |
105.00L |
76.19
|
No |
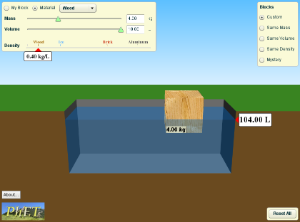
Green
|
4.00kg |
104.00L |
38.406 |
Yes |
Red
|
2.00kg |
102.00L |
19.607 |
Yes |
3. Looking at the
data on the previous page, what must be true about the density of
an object in
order for it to float? The object must be under .92kg/L, perhaps higher, but not as high as 2.00kg/L, in order for it to float.Same Density Section:
4. Calculate the density of the blue object in this section.
Mass ___3.00kg__________ Volume____103.00L___________ Density____29.126____________
5. Explain why both
the yellow and red objects float when they have different sizes. They may be made out of the same materials, such as aluminum.
Mystery Section:
6. Before you start,
pick an object that you think will float. StyrofoamPick an object that you think will sink. Brick
Material
|
Mass (kg)
|
Volume (L)
|
Density (kg/L)
|
Does it Float?
|
A
|
65.14 |
103.38 |
630.1025
|
No |
B
|
.64 |
100.64 |
6.359 |
Yes |
C
|
4.08 |
104.08 |
39.20 |
Yes |
D
|
3.10 |
103.10 |
30.067 |
Yes |
E
|
3.53 |
101.00 |
34.95
|
No |
7. In the Custom
section describe the difference between how Styrofoam and ice
floated. Also explain why you think this is the case? The volume remained almost exact.
8. In the Same Mass
Section discuss what was interesting about the blue object’s behavior in the
water. Although the object sank all the way to the bottom it did so slowly.
9. In the Mystery
Section, click on the “Show Table” button.
What is the most dense
object on the
list? Write its density as well. Gold; 19.3kg/L
10. List something
you learned from this activity. Even though some objects can have the same volume or even mass, they may, or may not float, or sink in the same way.
The three 4th grade science education standards that my Teaching Idea meets are:
1) Science Performance Standard A, Science Connections: A.4.3 When investigating a science-related problem, decide what data can be collected to determine the most useful explanations.
2) Science Standard B, Nature of Science: B.4.1 Use encyclopedias, source books, texts, computers, teachers, parents, other adults, journals, popular press, and various other sources, to help answer science-related questions and plan investigations.
3) Science Standard E, Earth and Space: E.4.5 Describe the weather commonly found in Wisconsin in terms of clouds, temperature, humidity, and forms of precipitation, and the changes that occur over time, including seasonal changes.
Green House Effects
How a Fourth Grader Can Help Support a Better Tomorrow
Goals: Students will have an introductory look into understanding what green house effects are and be able to identify how harmful gases have an effect on global warming.
Procedures:
1. Click on the following links to view a video of green house effects http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=LFNKfWyGxHw
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bSjRM8qNUEQ&feature=player_embedded
2. Draw and list how the sun rays effect the earth and how raidiation is formed.
Questions:
3. Write a hypothesis, or predict then write a possible hypothesis of wthy you think the heat index of summer 2012 in Wisconsinis so extreme?
4. How do C02 emissions affect the atmosphere?
5. How do scientists meausre C02?
6. Name some ways you can help stomp out the green house effects and educate others by helping the planet in your daily living?

